General Long-Term Maintenance Conditions
| Temperature: | 20 °C |
| Light source: | mix of warm-white & cool-white fluorescent lamps |
| Intensity: | 3200 lux (maximum) |
| Periodicity: | 12:12 Light/Dark Cycle |
To reduce the risk of losing newly acquired cultures, it is highly recommended to initially duplicate the Collection's long-term maintenance conditions. Please note that these general maintenance conditions are not designed for optimal algal growth rates or large quantities. For information on the best growth conditions and media, consult other literature or conduct your own experiments. Once a stock culture is established, subcultures can be used to test other conditions.
You can find additional details on the long-term culture maintenance conditions on the Culture Maintenance Guides page.
Preparation of Living Algal Strains For Orders
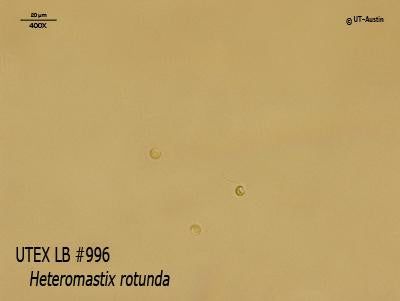
Approximately 15 mL aliquots of the stock maintained as a liquid culture are transferred to screwcap tubes. Quality control (QC) checks are then completed via microscopy.
Cultures are sealed and packaged in a temperature-regulating mailer and shipped the same day.
UTEX makes no attempt to quantify the number of organisms or other characteristics of the culture and only guarantees the identity of the organism as specified in the strain history.